Pythagorean Theorem Worksheets with Answers
3D Pythagoras (A)
Grades: 8th Grade, Geometry, IM 1
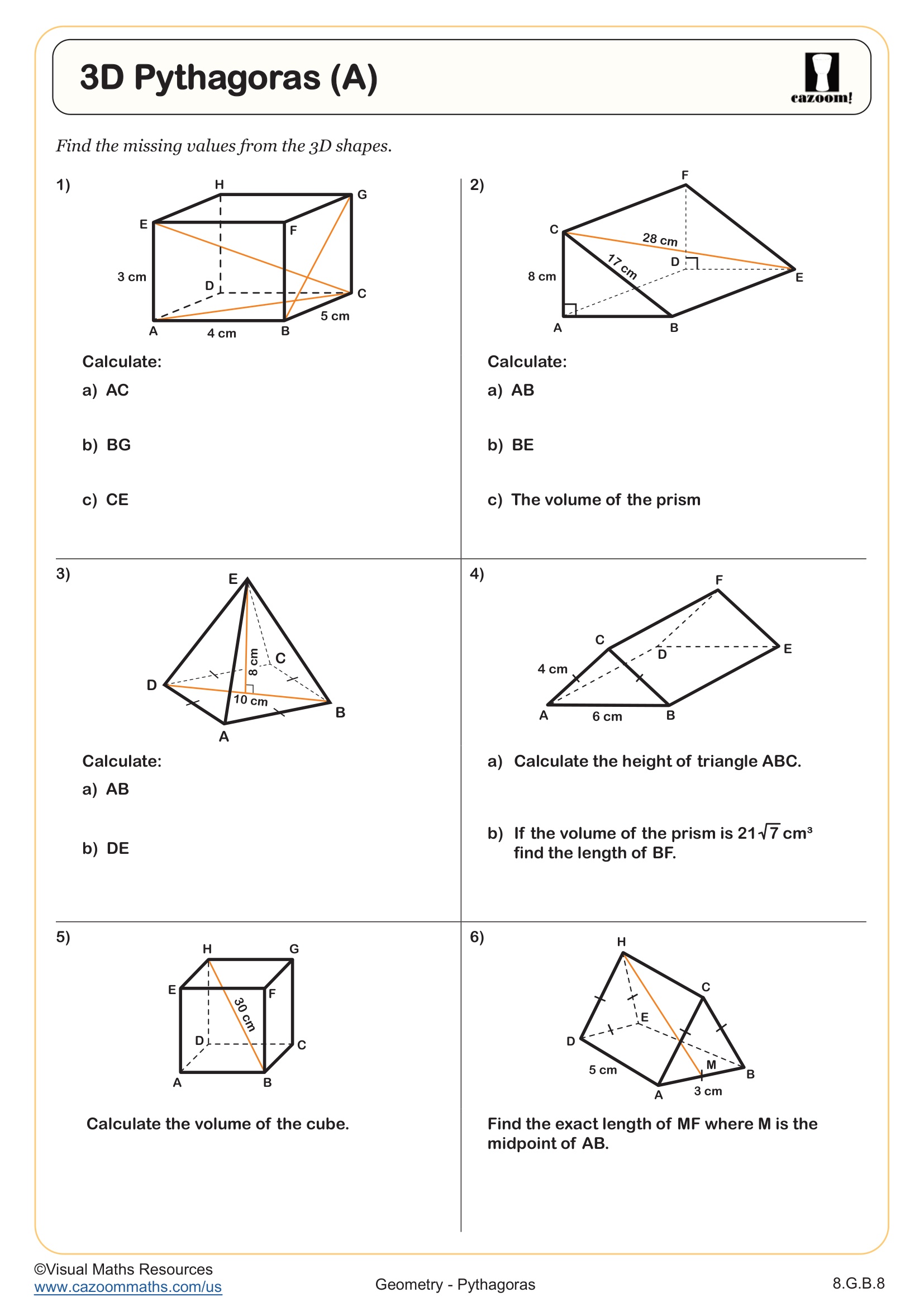
3D Pythagoras (B)
Grades: 8th Grade, Geometry, IM 1
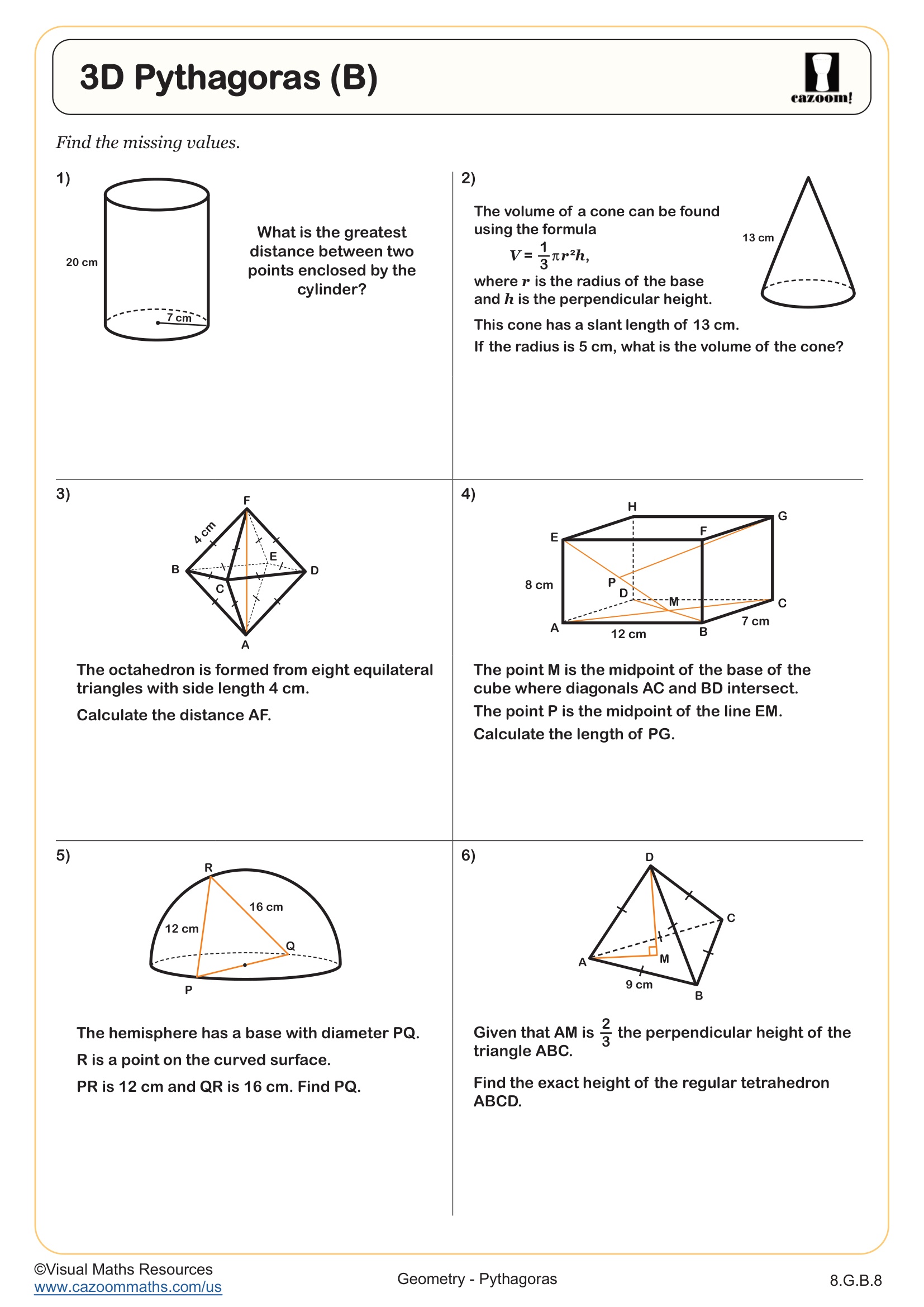
Identifying Right Triangles
Grades: 8th Grade
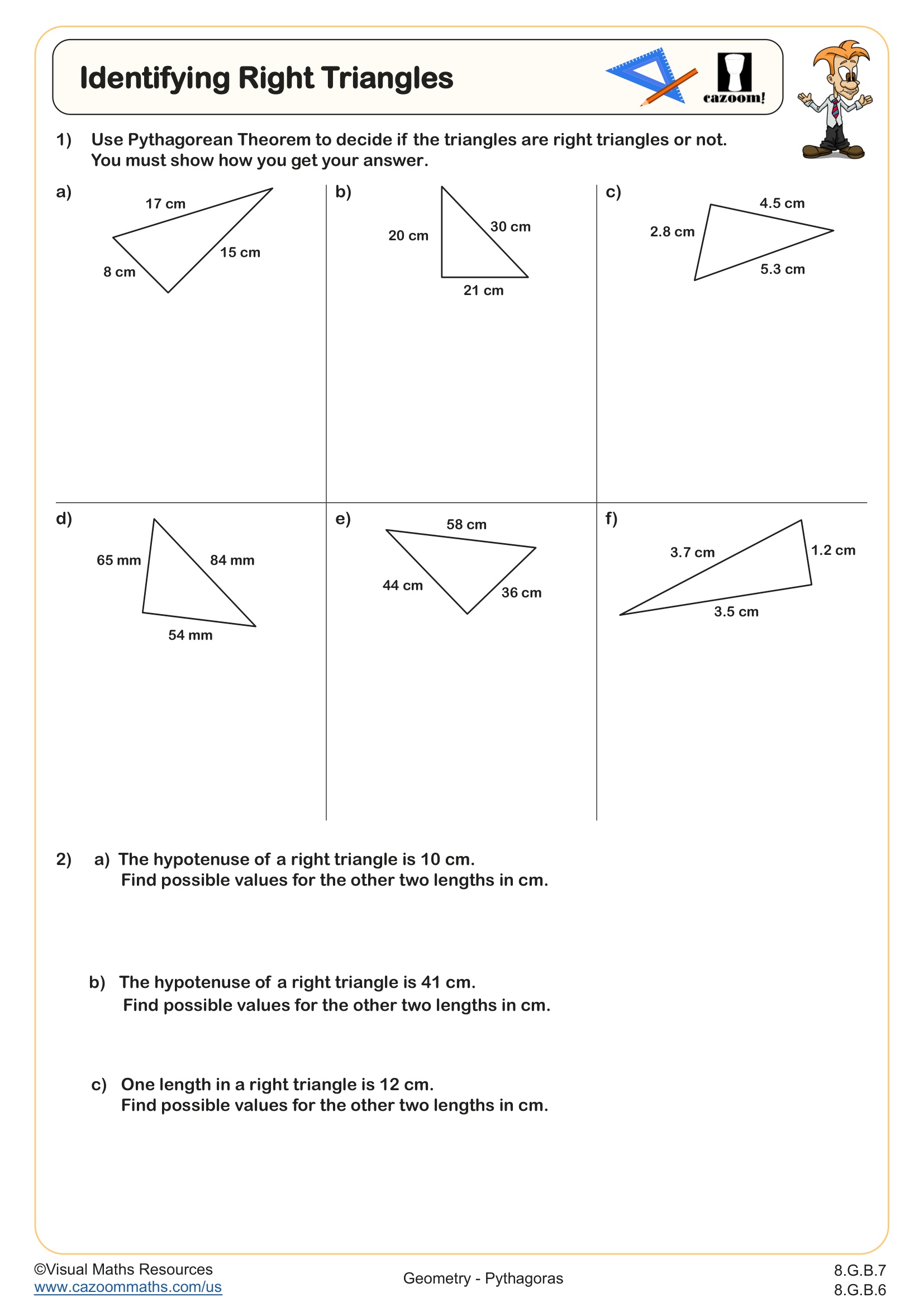
Multi Step Pythagorean Problems
Grades: 8th Grade, Geometry, IM 1
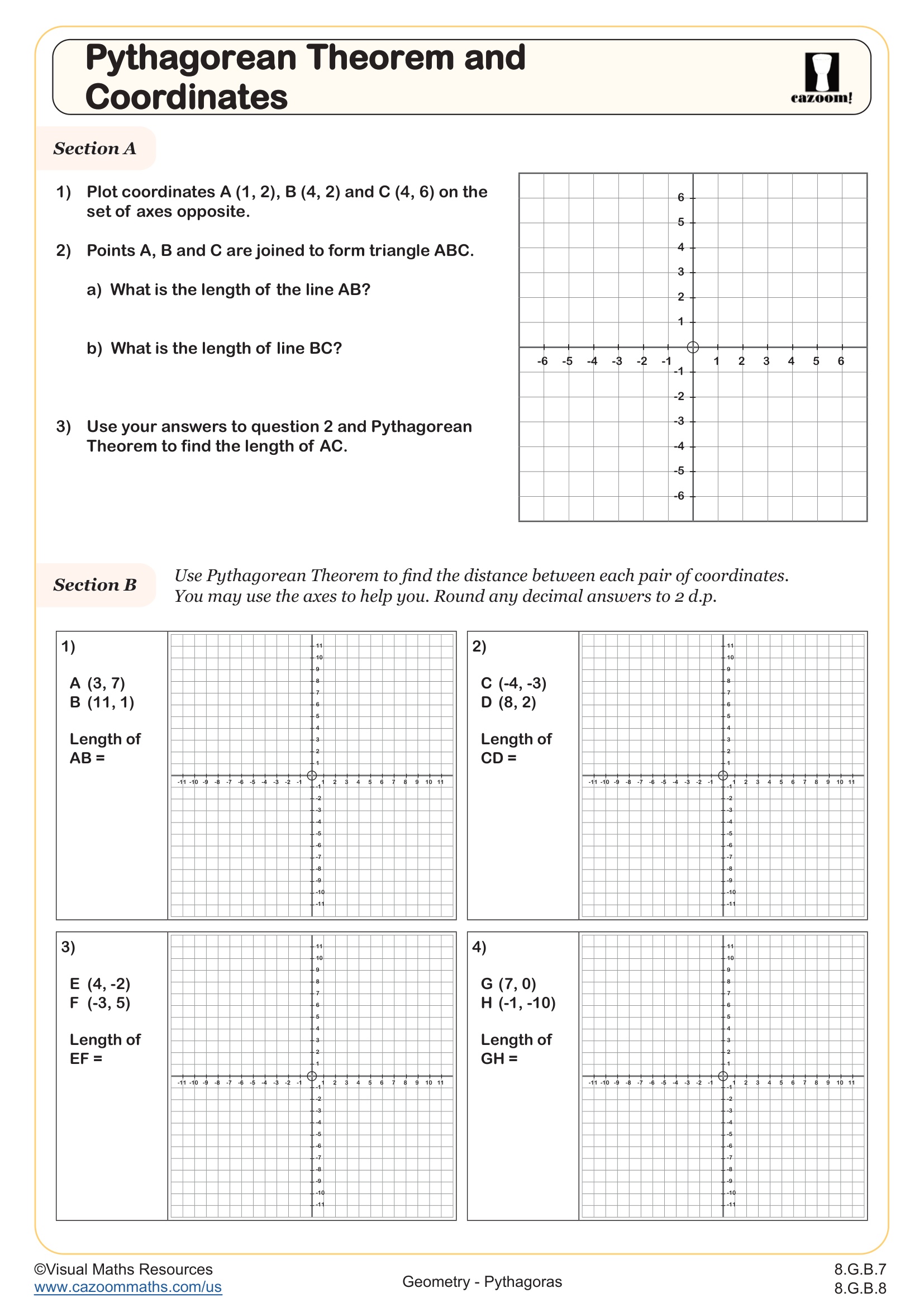
Pythagorean Theorem and coordinates
Grades: 8th Grade, Geometry, IM 1
Pythagorean Theorem Word Problems
Grades: 8th Grade

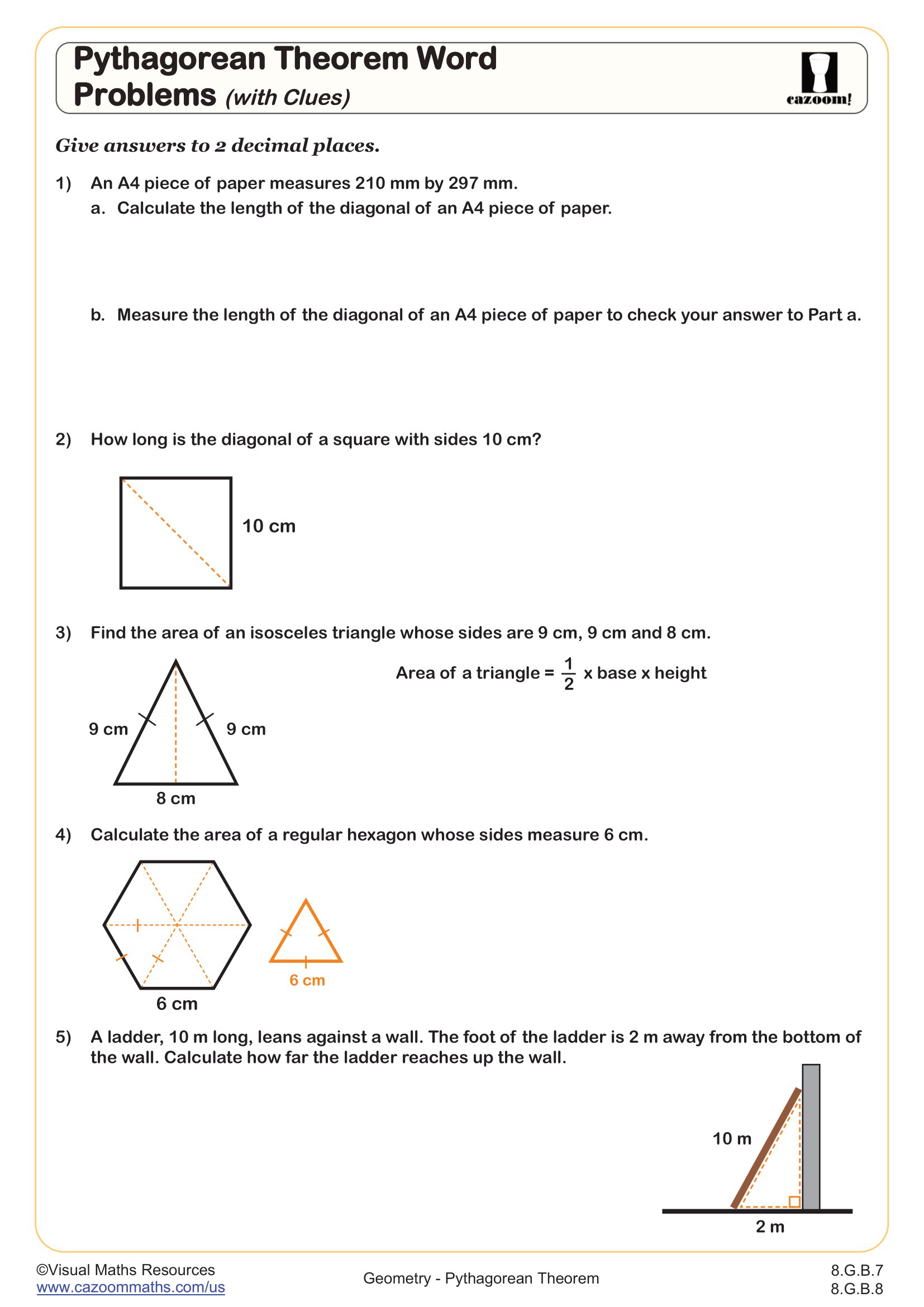
Pythagorean Theorem Word Problems (with clues)
Grades: 8th Grade
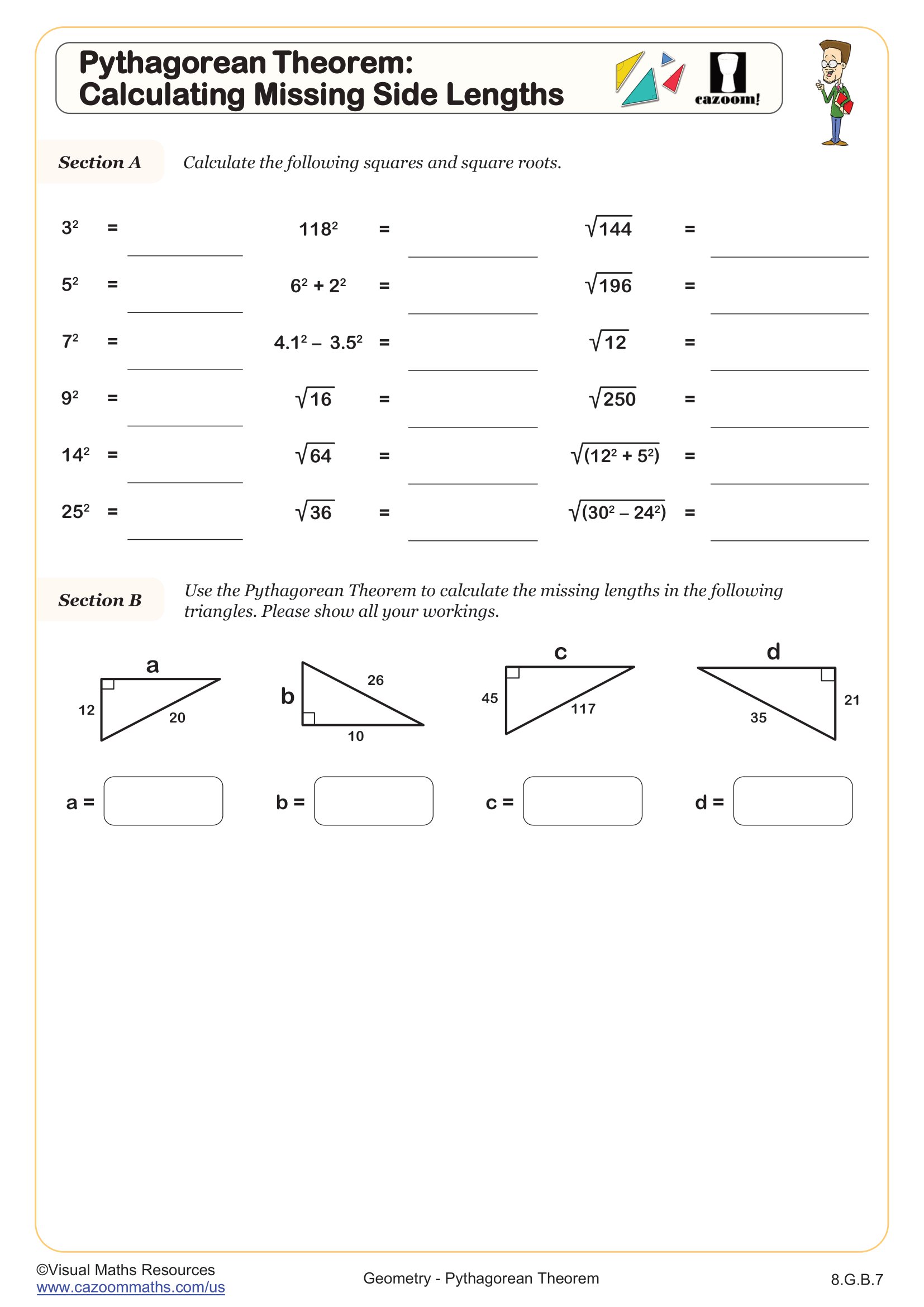
Pythagorean Theorem: Calculating Missing Side Lengths
Grades: 8th Grade
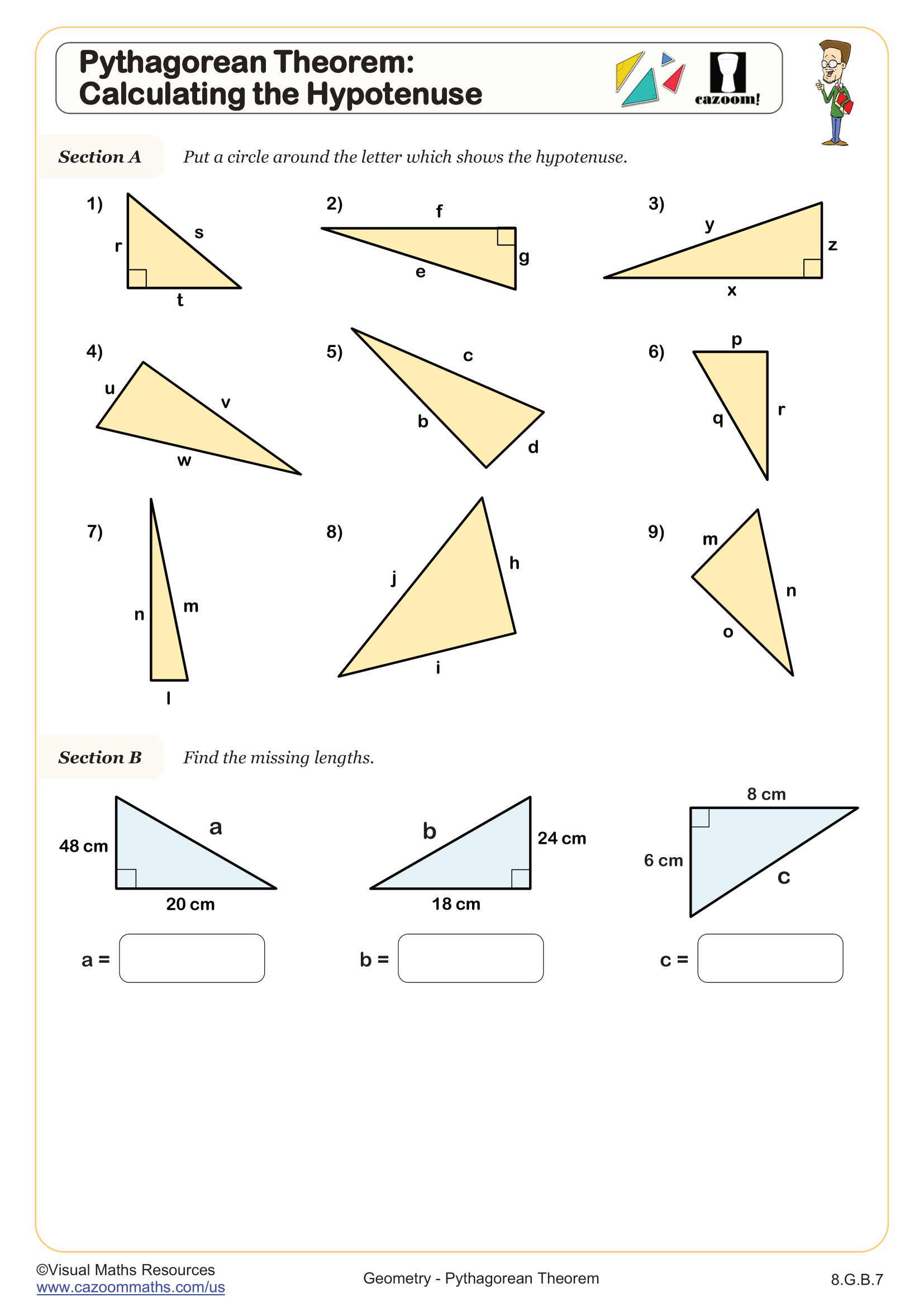
Pythagorean Theorem: Calculating the Hypotenuse
Grades: 8th Grade
All worksheets are created by the team of experienced teachers at Cazoom Math.
PRINTABLE PDF PYTHAGOREAN THEOREM WORKSHEETS WITH ANSWERS
Pythagorean Theorem is such a foundational part in Mathematics. From our Cazoom Math worksheets, your child can not only become familiar with the Pythagorean Theorem but can walk away as an expert, knowing how to apply their knowledge to solve real life problems. We can help support this by providing not only high-quality worksheets, but also answer keys to accompany the worksheets. By using the Pythagorean Theorem worksheets your students will easily find the length of any side of a right angled triangle.
DEFINITION OF PYTHAGOREAN THEOREM
The theorem is named after the Greek thinker Pythagoras, born around 570 BC. The theorem states that the area of the square whose side is the hypotenuse of a right angled triangle (the side opposite of the right angle) is equal to the sum of the areas of the squares on the other two sides. Written in algebraic notation this theorem gives the well-known equation . The in the equation represents the length of the hypotenuse, while and are the lengths of the other two sides of the triangle.
How to use the Pythagorean Theorem to solve an equation?
What follows is a step by step guide to find out the length of the missing side on right triangles. If you know the length of two sides on a right triangle it is really easy to find the length of the third one. Follow the explanation in the example:
12² + 9² = c²
(12×12) + (9×9) = c²
144 + 81 = c²
225 = c²
c² = √225
c = 15